 Infertility is generally defined as the inability to conceive after 12 months of trying without contraception, and may be a result of factors affecting the fertility of either partner.
In one third of cases, infertility is due to the woman (female factors); a third due to the man (male factors); and the remaining third no clear cause may be identified, which is termed unexplained infertility.
Women who get pregnant but have repeated miscarriages are also considered to be infertile.
It is well documented that over 80% of couples will conceive naturally within one year if they have regular, unprotected sex. A further 5-8% will achieve a pregnancy within two years of trying.
The most commonly recognised problems involve the production of the sperm, the release of eggs, or the mechanism by which the two meet for fertilisation.
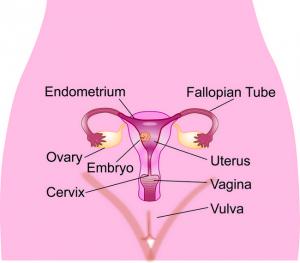
Conditions that may affect a woman’s fertility;
-
Tubal damage /Blocked fallopian tubes
-
Ovulatory problems
-
Endometriosis
-
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
-
Conditions affecting the uterus, such as fibroids
-
Congenital abnormalities (birth defects) involving the structure of the uterus.
-
Age – female fertility declines with age.
-
Medical conditions such as diabetes, epilepsy, thyroid and bowel diseases
-
Lifestyle factors such as stress, being overweight or underweight, smoking and alcohol consumption.
-
Having received medical treatment such as chemotherapy (drug treatment) or radiotherapy.
Conditions that may affect a man’s fertility; 
-
No sperm are produced (azoospermia)
-
A low number of sperm are produced (oligospermia)
-
Sperm are malformed or have poor motility (poor morphology/ motility)
-
Problems with the tubes carrying sperm,(congenital absence, damage by infection)
-
Problems getting an erection or ejaculating.(due to various medical /congenital conditions)
-
In rare cases, male infertility can be caused by a genetic disease, such as cystic fibrosis, or a chromosomal abnormality.
-
Having had surgery, for example, to correct a hernia, undescended testes or twisted testicles
-
Medial conditions e.g., Diabetes.
-
Lifestyle factors such as being overweight, smoking, alcohol consumption or having a job that involves contact with chemicals or radiation / high temperature or sitting for long time.
-
Male fertility is also thought to decline with age, although to what extent is unclear.
-
Having received medical treatment such as chemotherapy (drug treatment) or radiotherapy.
|









